- support@domain.tld
- +86051983732179
Selecting the right mold is critical in aluminum die casting, as it determines the part’s strength, precision, and performance. This guide explores the best mold types for aluminum casting, outlining their benefits and how to choose the ideal one for your project. Essential for technicians, managers, and buyers, this knowledge ensures the production of high-quality parts at scale
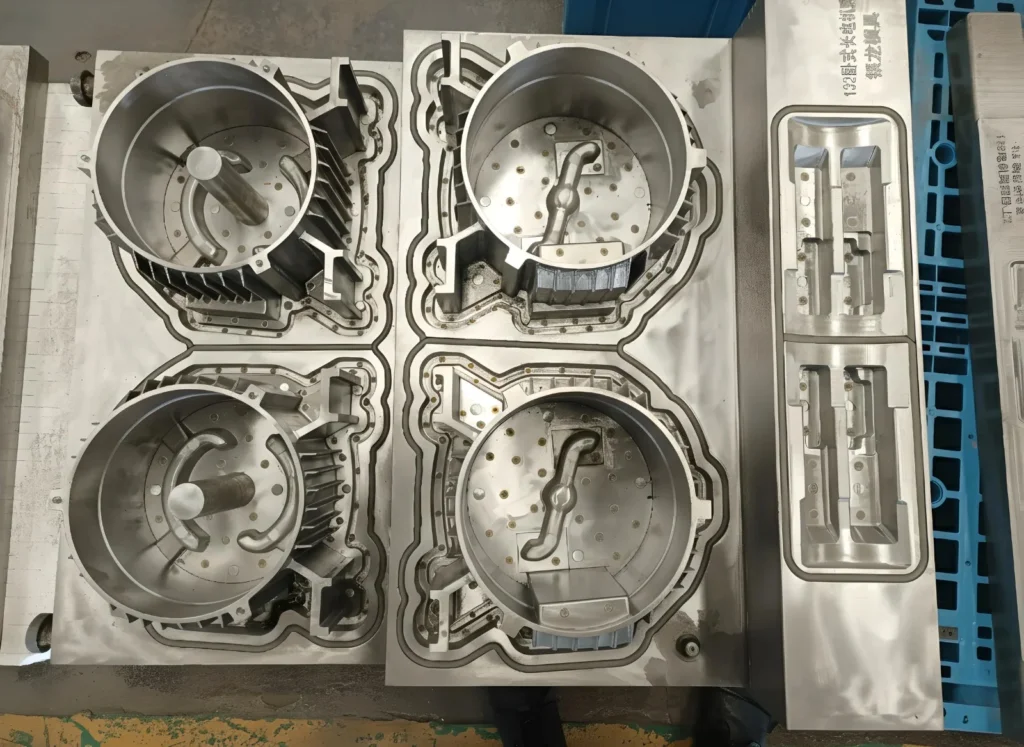
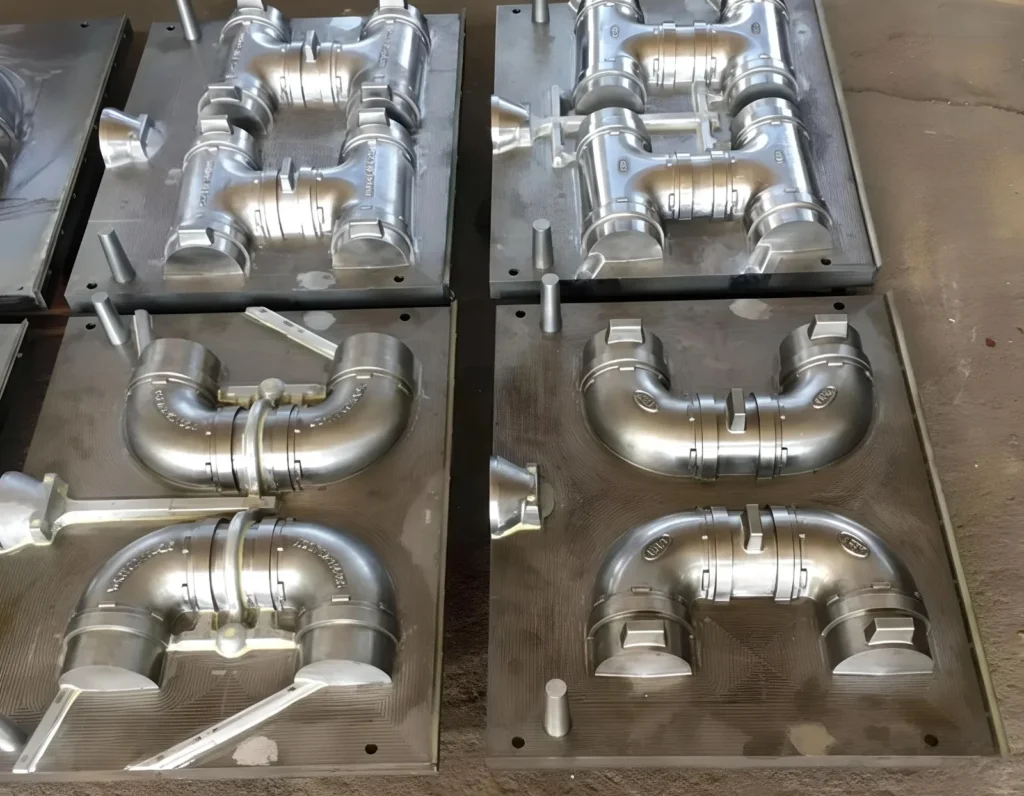
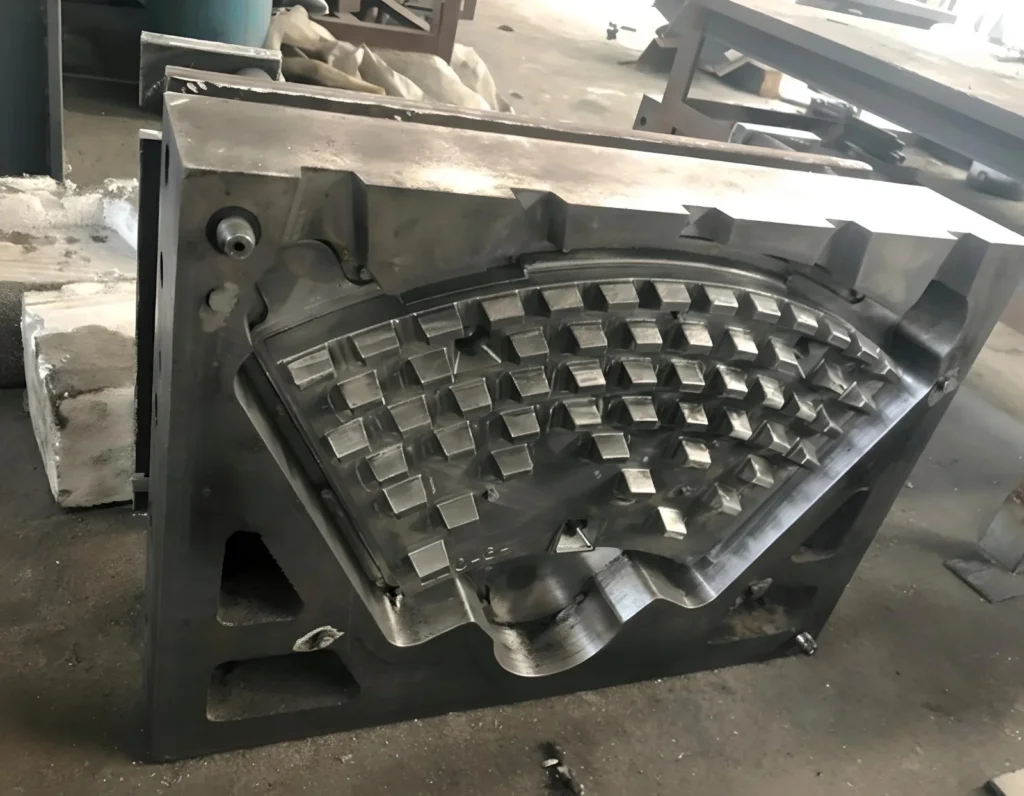


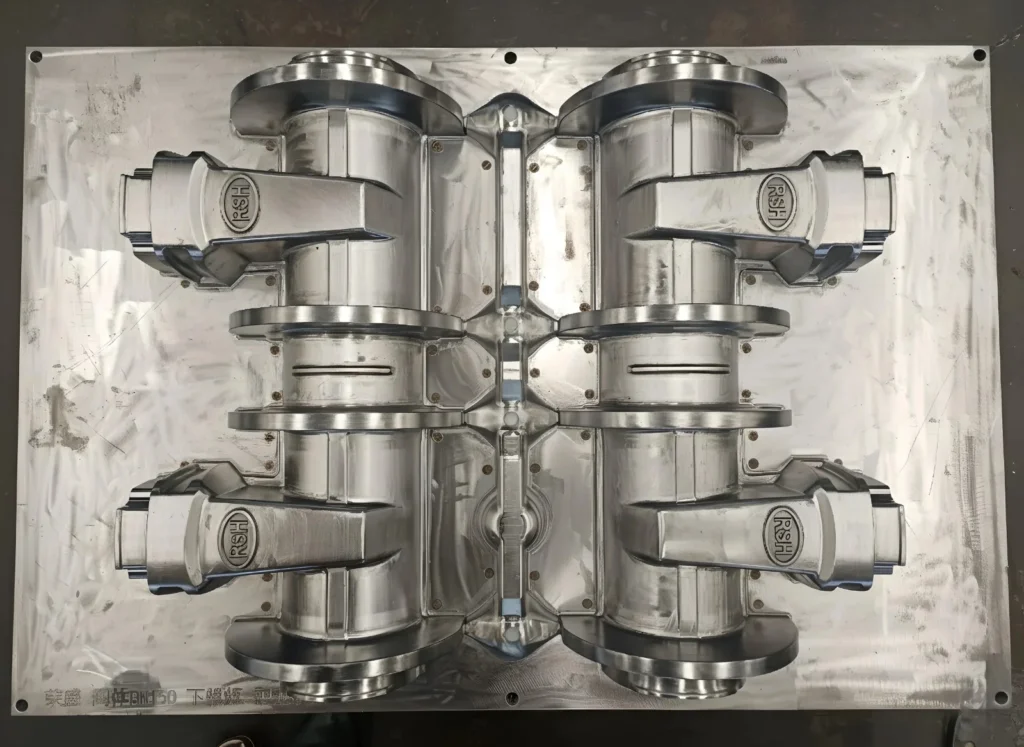
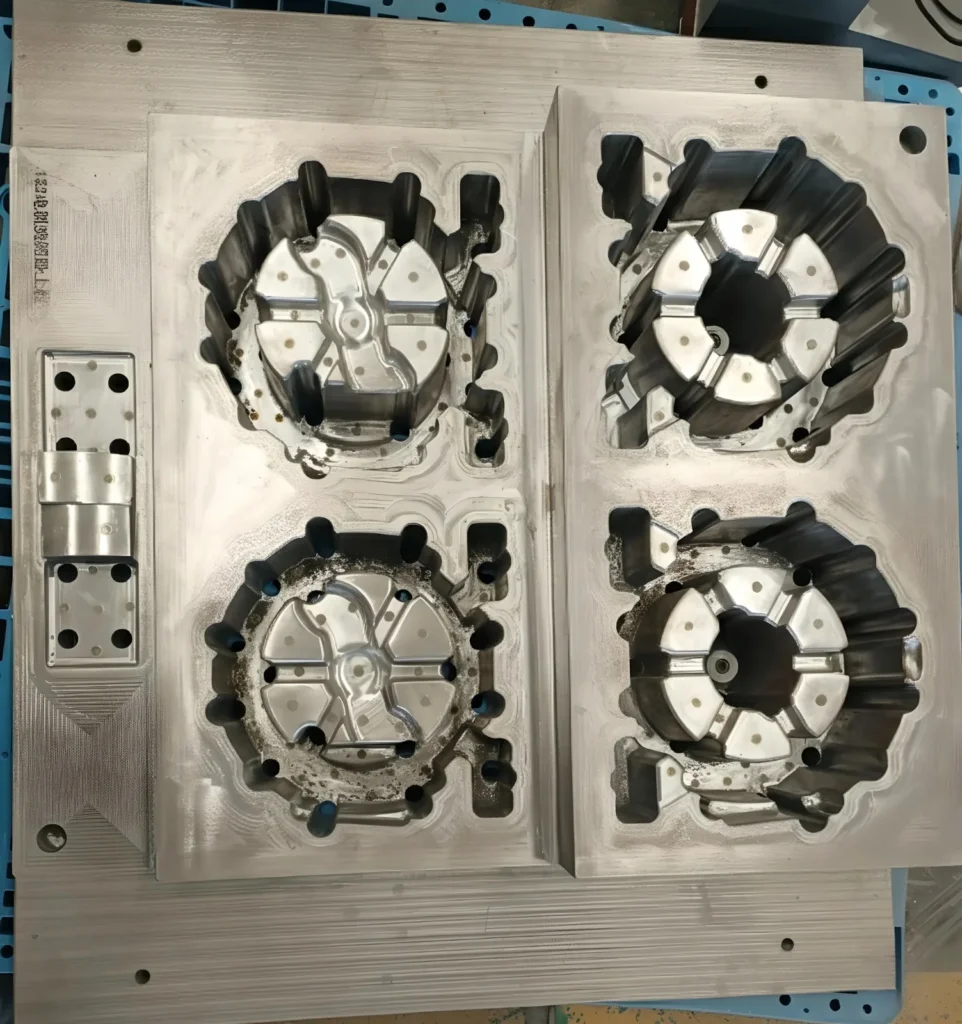

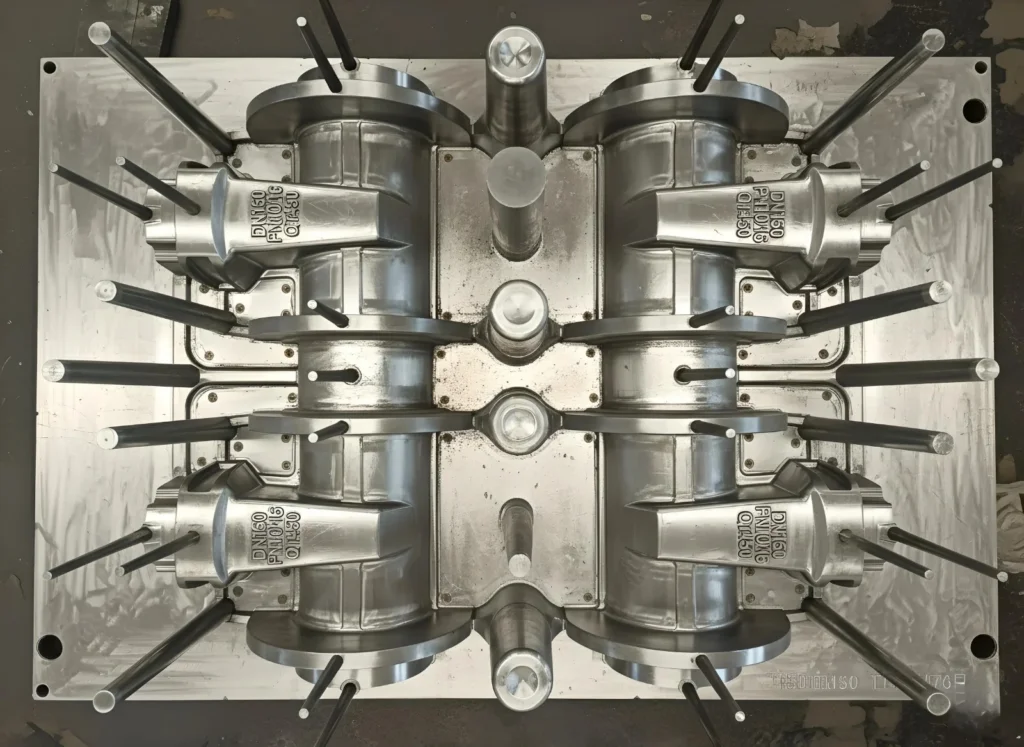


| Feature | Casting Mold (General) | Die Casting Mold (Specific) |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship | Broad category encompassing many processes. | A specific type of permanent mold used in one process. |
| Process Used In | Sand Casting, Investment Casting, Permanent Mold Casting, etc. | Die Casting only. |
| Mold Material | Sand, ceramic, plaster, or metal. | Hardened Tool Steel (almost exclusively). |
| Pressure | Often gravity or low pressure. | Very High Pressure injection (hundreds to thousands of psi). |
| Production Rate | Low to medium (except permanent mold). | Very High (fast cycle times). |
| Part Finish & Detail | Varies; can be rough (sand) to very good (investment). | Excellent surface finish, fine detail, thin walls. |
| Typical Materials | Ferrous & Non-ferrous metals, plastics, etc. | Primarily Non-ferrous alloys (Al, Zn, Mg). |
| Mold Cost | Low (sand) to High (permanent metal mold). | Extremely High (complex steel tooling). |
| Best For | Large parts, ferrous metals, low/medium volumes, prototypes. | High-volume, complex, thin-walled non-ferrous parts. |
The material used to manufacture aluminum die casting mold can significantly impact the casting process, influencing factors such as mold life, casting quality, and production speed. This is where it gets interesting… there’s a wide variety of materials available, each with its own set of advantages. Let’s take a closer look at the most commonly used materials for aluminum casting molds,
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Durable, heat-resistant, precise | Expensive | High-volume production |
| Iron | Good thermal conductivity, affordable | Shorter lifespan | Sand and permanent molds |
| Graphite | High thermal conductivity, precise | Expensive | Investment casting, detailed parts |
| Sand | Cost-effective, flexible | Low durability, limited precision | Simple or low-cost parts |
| Factor | Consideration | Mold Types |
|---|---|---|
| Product Size | Large/complex parts | Permanent molds, Die-casting molds |
| Production Volume | High production rate | Die-casting molds, Permanent molds |
| Mold Material | Durability, heat resistance | Steel, Graphite |
| Lead Time & Cost | Quick production and cost-effective | Sand molds, Investment molds |
| Mold Type | Best Use | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die-casting | High-volume production, complex shapes | High precision, smooth surfaces | High upfront cost, not suitable for large parts |
| Coating Type | Benefit | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Mold release, surface finish | Investment casting |
| Graphite | Improves aluminum flow | Die-casting, sand molds |
| Wax | Prevents reactions with mold | Investment casting |